-
Class Room Training
Hyderabad
-
Online Training
Join From Anywhere
-
Class Room Training
Hyderabad
-
Online Training
Join From Anywhere
Our Blog
How to build your own Android App -Step by Step Guide
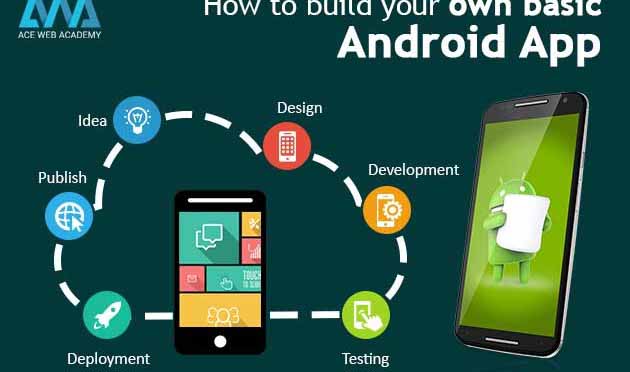
It’s the range of android apps now as every business gets success and reach the end users with its true potential. This is not down to earth process to create an outstanding app, rather every developer with basic knowledge of some coding languages like JAVA, C, C++ can do this.
So if you wanted to create an app out of your ideas, then here is the quick and simple guide which helps you to build your won android app guide in less time. Follow the simple steps and for sure you can earn handsome amount with the creative app which you have curated.
1. Prerequisites of android app development:
If you want to create a basic android app, you should have basic knowledge in coding languages like JAVA, C, C++
i) Concept/idea to showcase or implement your app
ii) System specifications to check:
The following are the required software requirements which you need to install if you are not having before you start creating the app. Doesn’t have!
“Download and install the both Java tool Kit and Android Studio”
First, we need to install Java Jdk, because android studio will select automatically jdk path.
Or
If you want to install android studio first then you need to set “Home path’
iii) Hardware Requirements: Ensure that you are having these hardware specifications – RAM 4GB, Hard disk 500GB
2. Wireframe:
Have a great idea to develop app? Then now draw wireframe for your basic app and ensure that you are making use of this tool to represent the proposed functionality of the app and the structure of the app.
There should be proper attention on the graphical elements and the functionality of the app. When this is achieved properly, then developing the code will be easier and you will also know how the end users are going to use it. It is also helpful to make desired changes if you wish things are not as per the specifications.
For example, I want to develop a basic Login Demo app with login & sign up buttons functionality. Here is my wireframe

3. Impeccable Design:
Design is the element which attracts the people. When they like the graphics and the colors used for the theme of the app, then they would spend some more time and know the details of the app or its services. So make sure that you are vigilant about the colors and as well the images and the graphics which you put into it.
4. Start development:
Once you are done with the wireframe and then added the images and the designs of the app, now it is time to start the coding as per the requirements.
Sources:
> How to Build Your First Mobile App & Make the Business Big With Apps
> Follow these Five Vital Steps of Building Mobile Application
Steps How to create android app (Login app Demo)
Step 1:
Open the Android studio and you can follow the bellow steps to create new app.
Go to file——->New —-> new project

Step 2: Define Your app name, package name.
Here you have to enter the app name, company domain and as well the package name once you are decided with the name.
App Name: Login Demo
Package/Domain Name: By default you can see your PC name.
package com.infasta.logindemo; here com is domain name, infasta(PC name) is user editable name and login demo is an app name

Step 3:
Enter the form Factors of the app (phone&tab, wear, tv, glass).
Form factor: It says the type of your app, In below image you can find options. Depends on the requirement you need to choose.

Step 4:
Once you select the form factor, the code will be generated by default.
Select empty activity for “Login App Demo”

Step 5:
After you selected the form empty form factor, java class(with default class name as MainActivity) and related xml file(with default name as activity_main)
As per your requirement, you change both Java class and xml file name.

Step 6: Build the Application
Once you finish step 5, your application starts building in back-end in this process dependence jar files will be added to app and completes app building.

Step 7:
Once your application is built project gets created and then Java Class, Xml files open automatically. You can see same as below

-:Code for Login app Demo:-
Step 8:
Open xml file, go to Design part and drag required two buttons from left side widgets window
Here you can define the button listener method inside button tag

android:onClick=“loginPage“
<!—onClick=signupPage this method name you can write inside the java class
end of onCreate() method –>
In text view you can see below code.
<?xml version=“1.0” encoding=“utf-8”?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
xmlns:tools=“http://schemas.android.com/tools”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
android:paddingBottom=“@dimen/activity_vertical_margin”
android:paddingLeft=“@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin”
android:paddingRight=“@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin”
android:paddingTop=“@dimen/activity_vertical_margin”
tools:context=“com.infasta.logindemo.MainActivity”>
<Button
style=“?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:text=“Login”
android:id=“@+id/SignUp”
android:layout_alignParentTop=“true”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true”
android:layout_marginTop=“108dp”
android:layout_alignParentRight=“true”
android:layout_alignParentEnd=“true”
android:onClick=“loginPage“/>
<!—onClick=loginPage this method name you can write inside the java class
end of onCreate() method –>
<Button
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:text=“Signup”
android:id=“@+id/button2”
android:layout_below=“@+id/SignUp”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true”
android:layout_alignRight=“@+id/SignUp”
android:layout_alignEnd=“@+id/SignUp”
android:onClick=“signupPage“/>
<!—onClick=signupPage this method name you can write inside the java class
end of onCreate() method –>
</RelativeLayout>
Step 9: You can define the button actions above the screen in java file.
Every screen’s logical code is provided here.
MainActivity.java
package com.infasta.logindemo;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
//login button method
public void loginPage(View v){
Intentintent=new Intent(this,LoginActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
//signup button method
public void signupPage(View v){
Intentintent=new Intent(this,LoginActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
How to create the new Activity or another screen
Step 10: To create new Activity, follow the below screen and here you can defend the java class, xml file name also.


Step 11:
This is the screen for (Login screen) xml files
activity_login.xml
<?xml version=“1.0” encoding=“utf-8”?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
xmlns:tools=“http://schemas.android.com/tools”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
android:paddingBottom=“@dimen/activity_vertical_margin”
android:paddingLeft=“@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin”
android:paddingRight=“@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin”
android:paddingTop=“@dimen/activity_vertical_margin”
tools:context=“com.infasta.logindemo.LoginActivity”>
<EditText
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:id=“@+id/editText”
android:layout_alignParentTop=“true”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true”
android:layout_marginTop=“77dp”
android:layout_alignParentRight=“true”
android:layout_alignParentEnd=“true”
android:hint=“user name”/>
<EditText
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:id=“@+id/editText2”
android:layout_below=“@+id/editText”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true”
android:layout_alignRight=“@+id/editText”
android:layout_alignEnd=“@+id/editText”
android:hint=“password”/>
<Button
style=“?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:text=“Login”
android:onClick=“homePage”
android:id=“@+id/button”
android:layout_below=“@+id/editText2”
android:layout_centerHorizontal=“true” />
</RelativeLayout>
java file : LoginActivity.java
package com.infasta.logindemo;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class LoginActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
EditTextnameEdt,passEdt; //user reference variable names
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_login);
//register the editText id’s and type cast to xml id’s
nameEdt=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText);
passEdt=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText2);
}
public void homePage(View v){
//navigation one screen to another screen
//current class and target class name
Intent intent=new Intent(this,LoginActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
}

Step 12:
This screen is for (signup screen) java and xml files
Activity_signup.xml
<?xml version=“1.0” encoding=“utf-8”?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
xmlns:tools=“http://schemas.android.com/tools”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
android:paddingBottom=“@dimen/activity_vertical_margin”
android:paddingLeft=“@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin”
android:paddingRight=“@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin”
android:paddingTop=“@dimen/activity_vertical_margin”
tools:context=“com.infasta.logindemo.SignUpActivity”>
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge”
android:text=“New User”
android:id=“@+id/textView”
android:layout_alignParentTop=“true”
android:layout_centerHorizontal=“true”
android:layout_marginTop=“54dp” />
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge”
android:text=“Name”
android:id=“@+id/textView2”
android:layout_below=“@+id/textView”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true”
android:layout_marginTop=“50dp” />
<EditText
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:id=“@+id/editText3”
android:layout_alignBottom=“@+id/textView2”
android:layout_alignLeft=“@+id/textView”
android:layout_alignStart=“@+id/textView” />
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge”
android:text=“Phone”
android:id=“@+id/textView3”
android:layout_alignBottom=“@+id/editText4”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true” />
<EditText
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:inputType=“phone”
android:ems=“10”
android:id=“@+id/editText4”
android:layout_below=“@+id/editText3”
android:layout_alignRight=“@+id/editText3”
android:layout_alignEnd=“@+id/editText3” />
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge”
android:text=“Password”
android:id=“@+id/textView4”
android:layout_alignBottom=“@+id/editText5”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true” />
<EditText
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:inputType=“textPassword”
android:ems=“10”
android:id=“@+id/editText5”
android:layout_below=“@+id/editText4”
android:layout_alignLeft=“@+id/editText4”
android:layout_alignStart=“@+id/editText4” />
<Button
style=“?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:text=“signup”
android:id=“@+id/button3”
android:layout_below=“@+id/textView4”
android:layout_alignRight=“@+id/textView”
android:layout_alignEnd=“@+id/textView”
android:layout_marginTop=“40dp”
android:onClick=“signup”/>
</RelativeLayout>
java file for SignupAcitvity.java
package com.infasta.logindemo;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class SignUpActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
EditText nameEdt,passEdt,phoneEdt; //user reference variable names
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sign_up);
//register the editText id’s and type cast to xml id’s
nameEdt=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText3);
passEdt=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText4);
phoneEdt=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText5);
}
//button
public void signup(View v){
//get the values from edit text
String name=nameEdt.getText().toString();
String pass=passEdt.getText().toString();
String phone=phoneEdt.getText().toString();
//navigation one screen to another screen
//current class and target class name
Intent intent=new Intent(this,HomeActivity.class);
//put the values from Intent
intent.putExtra(“key1”,name);//key and value pair
intent.putExtra(“key2”,pass);
intent.putExtra(“key3”,phone);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
Step 13:
How to pass the values from one screen to another screen
Here the above signup details are shown as followed.
Ctivity_home.xml
<?xml version=“1.0” encoding=“utf-8”?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
xmlns:tools=“http://schemas.android.com/tools”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
android:paddingBottom=“@dimen/activity_vertical_margin”
android:paddingLeft=“@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin”
android:paddingRight=“@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin”
android:paddingTop=“@dimen/activity_vertical_margin”
tools:context=“com.infasta.logindemo.HomeActivity”>
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge”
android:text=“Name:”
android:id=“@+id/textView5”
android:layout_alignParentTop=“true”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true”
android:layout_marginTop=“96dp” />
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium”
android:text=“Medium Text”
android:id=“@+id/textView6”
android:layout_alignTop=“@+id/textView5”
android:layout_alignParentRight=“true”
android:layout_alignParentEnd=“true” />
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge”
android:text=“password”
android:id=“@+id/textView7”
android:layout_below=“@+id/textView5”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true” />
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium”
android:text=“Medium Text”
android:id=“@+id/textView8”
android:layout_below=“@+id/textView5”
android:layout_alignRight=“@+id/textView6”
android:layout_alignEnd=“@+id/textView6” />
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge”
android:text=“Phone”
android:id=“@+id/textView9”
android:layout_below=“@+id/textView7”
android:layout_alignParentLeft=“true”
android:layout_alignParentStart=“true” />
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:textAppearance=“?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium”
android:text=“Medium Text”
android:id=“@+id/textView10”
android:layout_alignTop=“@+id/textView9”
android:layout_alignLeft=“@+id/textView8”
android:layout_alignStart=“@+id/textView8” />
</RelativeLayout>
java file HomeActivity.java
package com.infasta.logindemo;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class HomeActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextViewname,pass,phone;//user reference variable names
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_home);
//register the editText id’s and type cast to xml id’s
name=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView6);
pass=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView8);
phone=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView10);
//get the values from Intent
Intent intent=getIntent();
//Display the values
//key1,key,key2,key3=intent key’s name
name.setText(intent.getStringExtra(“key1”)); pass.setText(intent.getStringExtra(“key2”));
phone.setText(intent.getStringExtra(“key3”));
}
}
Congrats! You Completed Your Basic App building, check demo.
Conclusion:
This is the simple guide which helps even the beginners to develop an app which gets the attention of the market. If you have an idea for business, do not stop implementing it just thinking of the budget. Because you can even create an app and this is as simple as explained above. Just make a note of the factors and the functionality and then you can achieve step by step in no time. Happy and successful journey of creating the app for your simple business.
About Author: Raju, passionate about app development. He professional Mobile app development trainer at Ace Web Academy, having 5 years of experience in real-time app development.
Categories
Copyright 2025 © acewebacademy.com. All Rights Reserved. A division of Infasta Soft Solutions Pvt. Ltd.



